Table of Contents
ToggleWhen it comes to medical terminology, few prefixes pack as much punch as “cyan/o.” This little blue word isn’t just a color; it’s a signal that something might be amiss in the body. Think of it as the medical world’s way of saying, “Hey, pay attention!” Whether it’s a sign of oxygen deprivation or a clue in diagnosing a condition, understanding “cyan/o” can turn a puzzling symptom into a clearer picture.
Overview of Cyan/o Medical Term
Cyan/o is a medical prefix derived from the Greek word “kyanós,” meaning blue. Medical terminology often uses this prefix to describe conditions that result in a blue discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes. This discoloration typically occurs due to low oxygen levels in the blood, a condition known as cyanosis.
Cyanosis can present in various forms, including central and peripheral cyanosis. Central cyanosis affects the core of the body, including the lips and trunk. It often indicates systemic issues, like respiratory or cardiac conditions. Peripheral cyanosis, on the other hand, occurs in the extremities, such as fingers and toes. This form usually stem from reduced blood flow in cases like shock or hypothermia.
Recognizing cyanosis is crucial for healthcare professionals. Effective identification can lead to swift intervention and diagnosis. Various medical conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or congenital heart defects, may present with cyanotic symptoms. Clinicians should note that not all blue discoloration signifies cyanosis; some skin conditions or external factors can also contribute to similar appearances.
Understanding the cyan/o prefix helps medical professionals convey critical information about a patient’s condition. In cases of unexplained cyanosis, immediate diagnostic evaluations are essential. Assessing oxygen saturation through pulse oximetry provides valuable insights. Evaluating symptoms, medical history, and additional diagnostics aids healthcare providers in determining underlying causes effectively.
Significance of Cyan/o in Medicine
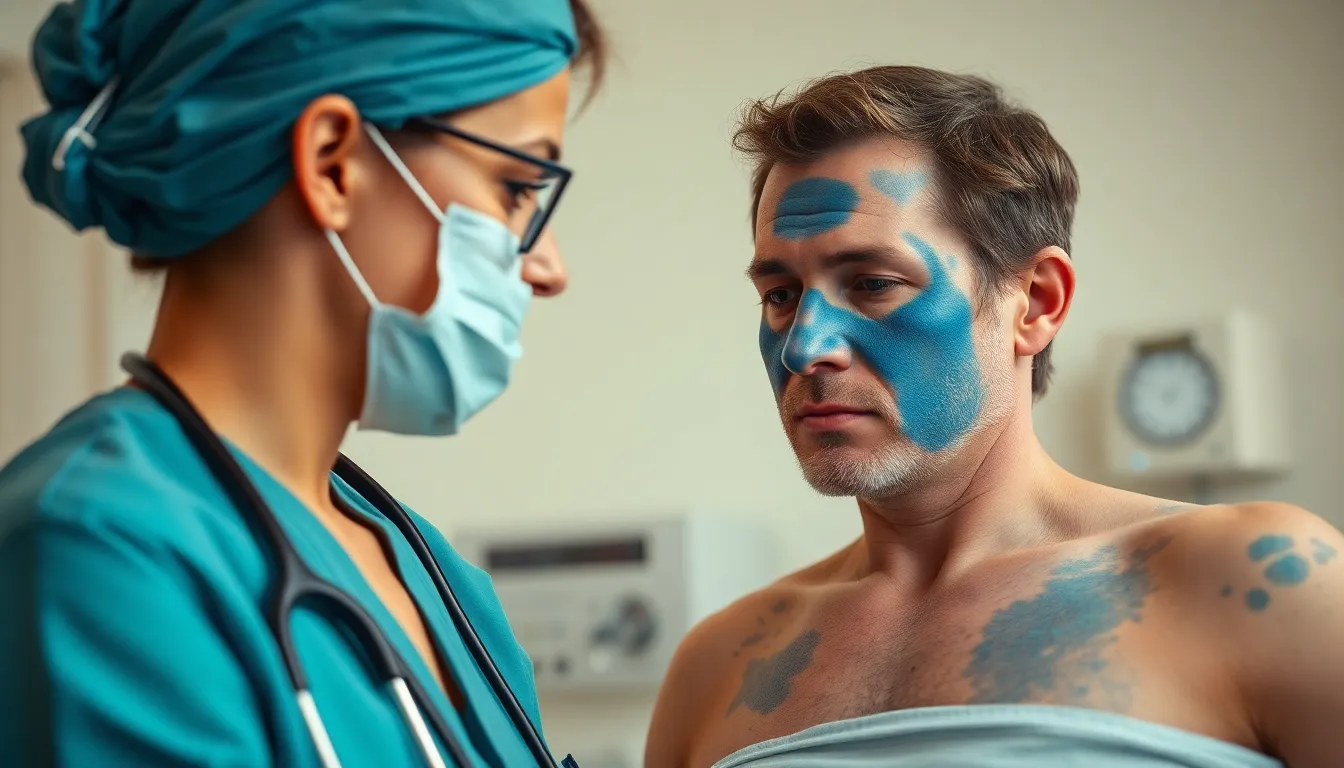
The prefix “cyan/o” holds significant value in the medical field. It denotes blue coloration, often a vital indicator of underlying health issues related to oxygen levels.
Clinical Implications
Central cyanosis affects the body’s core, indicating severe respiratory or cardiac conditions. Healthcare providers observe peripheral cyanosis in the extremities, which reflects reduced blood flow but can signal less urgent issues. Identification of cyanosis serves as a critical alert for urgent medical intervention. Patients presenting with blue discoloration may require immediate evaluation to identify respiratory distress or cardiac anomalies. Recognizing these presentations leads to timely treatment and improved outcomes.
Diagnostic Uses
Cyanosis aids in diagnosing various medical conditions. Healthcare professionals assess respiratory function by measuring oxygen saturation levels, which reveal the presence of cyanosis. A blue tint in mucous membranes and skin leads to further testing, including imaging studies or blood gas analyses. Physicians often use cyanosis as a diagnostic marker, guiding decisions regarding immediate care. Identifying the type of cyanosis—central or peripheral—helps streamline diagnostic pathways and informs treatment strategies.
Conditions Associated with Cyan/o
Cyan/o is closely associated with various medical conditions that result in blue discoloration. Identifying these conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Cyanosis
Cyanosis signifies a blue tint in the skin or mucous membranes, often appearing due to low oxygen levels in the blood. Central cyanosis affects the lips and trunk, indicating serious systemic issues like respiratory failure or congenital heart defects. Peripheral cyanosis, however, appears in extremities and usually points to reduced blood flow. Common causes include exposure to cold or reduced circulation. Observing the type of cyanosis helps healthcare providers determine whether immediate intervention is necessary.
Other Related Disorders
Several disorders can accompany or mimic cyanosis effects. Conditions such as hypoxia involve insufficient oxygen reaching tissues, leading to similar blue discoloration. Additionally, methemoglobinemia results from abnormal hemoglobin that cannot carry oxygen effectively, causing cyanotic symptoms. Another related condition is pulmonary embolism, where blood clots affect lung circulation, triggering acute cyanosis. Identifying these related disorders enhances understanding and aids in prompt management strategies for patients experiencing symptoms.
Treatment Approaches Involving Cyan/o
Cyan/o-related conditions require prompt and effective treatment strategies. Medical interventions and lifestyle changes play crucial roles in managing symptoms and improving patient outcomes.
Medical Interventions
Healthcare professionals often utilize supplemental oxygen to address the underlying issues associated with cyanosis. In cases of respiratory failure, mechanical ventilation might become necessary to assist breathing. Medications can include bronchodilators or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation in the airways. For congenital heart defects or significant circulatory problems, surgical options may provide effective solutions. Blood tests help identify conditions such as methemoglobinemia, allowing for targeted treatments. These interventions aim to restore normal oxygen levels and improve overall health.
Lifestyle Changes
Modifying lifestyle choices can significantly impact individuals experiencing cyanosis. Quitting smoking enhances lung function and oxygen saturation levels. Staying active with aerobic exercises improves cardiovascular health and blood circulation. Maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants supports overall well-being and can improve oxygen transport. Hydration plays a vital role in maintaining optimal blood flow and overall bodily functions. Regular monitoring of health status helps individuals detect changes in symptoms early, facilitating timely medical consultations. These adjustments contribute to better management of cyan/o-related conditions.
Understanding the medical term “cyan/o” is essential for recognizing serious health issues related to oxygen deprivation. The prefix serves as a vital tool for healthcare professionals in diagnosing conditions that manifest as a blue discoloration of the skin or mucous membranes. By differentiating between central and peripheral cyanosis, practitioners can swiftly identify underlying problems and implement appropriate treatment strategies.
Timely recognition of cyanosis not only aids in immediate medical intervention but also enhances overall patient outcomes. Awareness of related conditions and effective management approaches further underscores the importance of this term in clinical practice. By prioritizing education around cyanosis, both healthcare providers and patients can work together towards improved health and well-being.